
Meet the Creatures and Creators Behind Bali’s Parade for Banishing Evil Spirits
On the night before the Balinese New Year, villagers bring monsters to life—and then burn them.
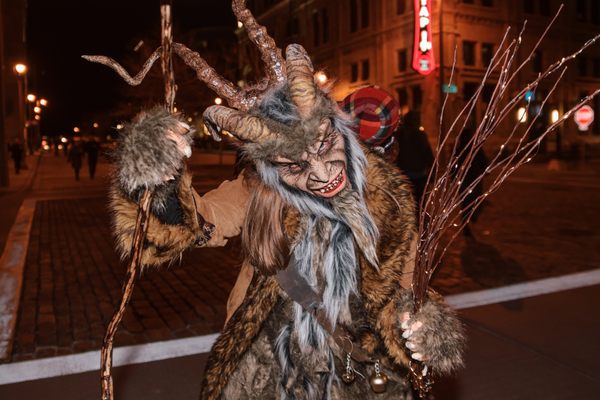
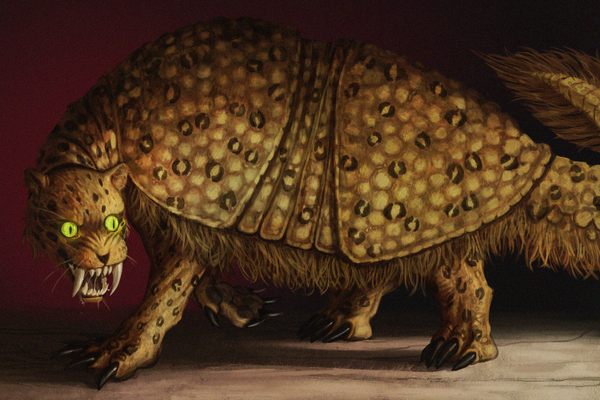
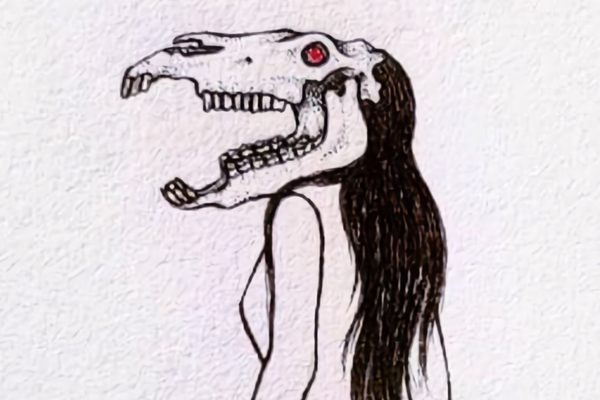
On the eve of March 11, the streets of the traditional village of Mengwi, Bali, flooded with monsters. The giant figures loomed over villagers’ heads, with grotesque smiles, protruding fangs, and extra arms and eyes. They danced in the night, each one brought to life by dozens of locals who moved as one, lifting, spinning, and shaking the monstrous creations.
The spectacle, known as the Ngrupuk parade, is one of several rituals meant to banish evil ahead of Nyepi and the Balinese New Year. While Nyepi is a day of mandatory rest and meditation for Balinese Hindus, the night before is quite the opposite.
The monstrous figures known as ogoh-ogoh—meaning to shake—represent Bhuta-Kala, evil spirits that need banishing, according to Balinese Hindu tradition. The figures, some as tall as a two-story building, are carried boisterously through town on bamboo platforms before their fiery demise.

Ngrupuk is a rather new Nyepi ceremony; ogoh-ogohs first appeared in Bali’s capital city Denpasar in the early 1980s. Since then, the annual parade has spread to surrounding villages. Local youth organizations build and carry the demonic effigies, and most crafters are teenagers and young men. Young children sometimes give creating a monster their best shot, while older master craftsmen are typically responsible for the most ornate ogoh-ogoh.
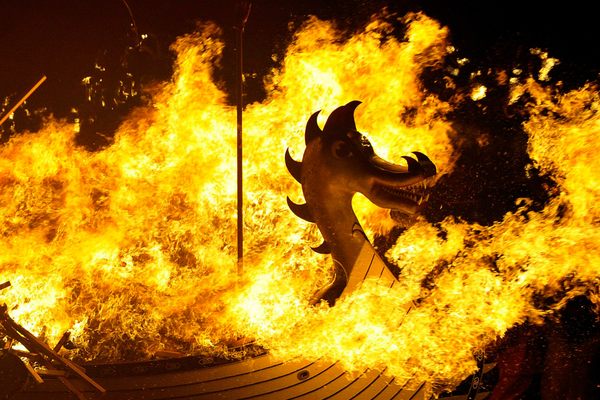
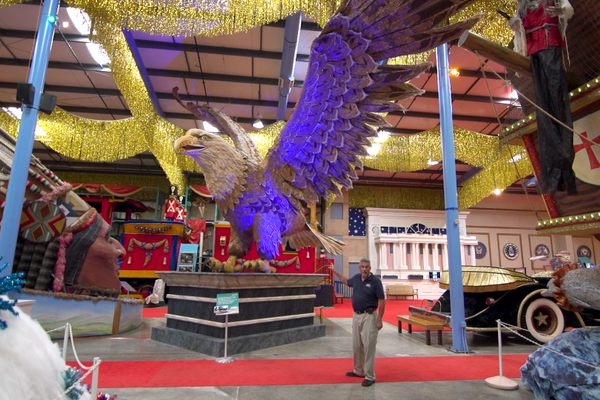
The monsters are traditionally burned at the end of the ceremony as an act of purification, but local painter and ogoh-ogoh collector I Ketut Nuada adds a few monsters each year to his growing collection-turned-museum.
Nuada once made ogoh-ogoh, but now leaves it to younger crafters and focuses instead on rounding up a few of his favorites after each parade. He collects whatever he can afford from among the effigies that survive a night of violent shaking. Over the last 12 years, Nuada has filled every inch of a warehouse in Mengwi with rescued and retired demons, some 31 in total.
“Every year there are more… and more technology,” says Nuada, speaking through a translator. The figures are traditionally made from paper, bamboo, and found materials, and brought to life through vigorous shaking. But in recent years, crafters have been experimenting with using electronics to light the monsters’ eyes, turn their heads, or raise their wings.

Anywhere from one to 10 people craft a single ogoh-ogoh between January and March. It takes dozens more to bring the demons to life. Before the event, disciples from the village temple will bless the ogoh-ogoh in a ritual where ceremonial offerings, called banten, are also presented.
Then the heavy lifting begins. Each figure is carried—along with lights and generators—by up to 40 locals on a raft-like bamboo platform. Dozens more walk ahead of the ogoh-ogoh carrying torches, or stand on the route performing traditional music. Everyone else gathers to take in the spectacle.
While many ogoh-ogoh will end their night in flames, some are stored away to be refurbished and sold for the following year, or—if they’re lucky—end up in Nuada’s collection. Photographer Matjaž Tančič captured the passionate creators, performers, and collectors who came together for Mengwi’s 2024 Ngrupuk event.



























Follow us on Twitter to get the latest on the world's hidden wonders.
Like us on Facebook to get the latest on the world's hidden wonders.
Follow us on Twitter Like us on Facebook